Current and Voltage Monitoring in Photovoltaic Installations

Fewer Decentralized Measuring Points Required in Solar Parks
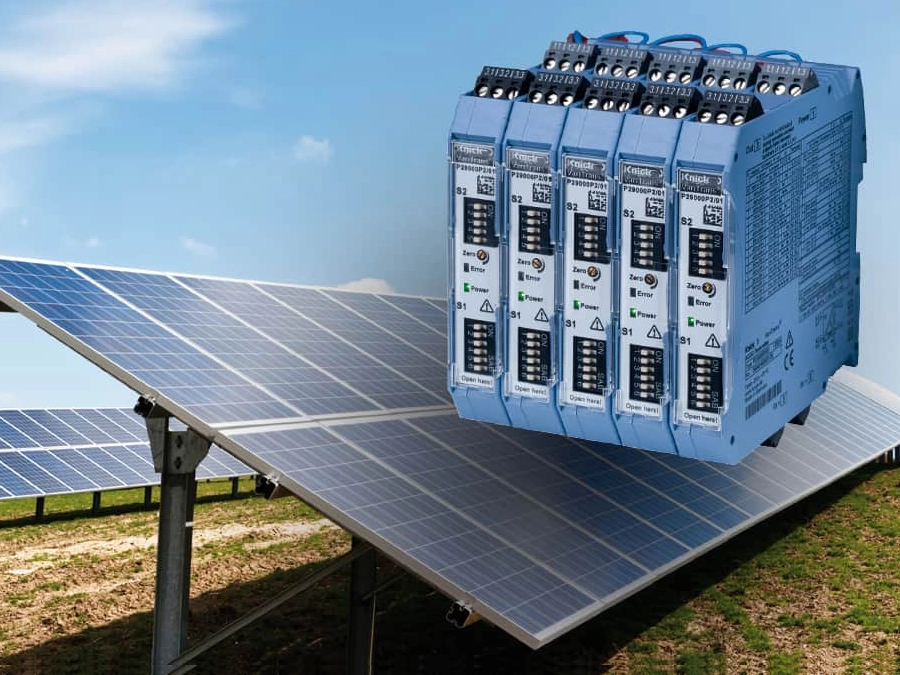
Solar parks are an essential component of the global energy transition. As a result, their expansion marches on relentlessly. For system operators, the priority is always the efficiency of their solar parks: Achieving higher output and better efficiency while keeping costs low. Transitioning the system voltage from 1,000 V DC to 1,500 V DC appears to be the logical consequence. Operators can achieve both economic and safety advantages by using high quality high-voltage measurement technology in the inverter stations.
Inverters: The Cornerstone of Every Photovoltaic (PV) Installation
Inverters are a key component of every solar park. They convert the direct current of the PV module into alternating current and then feed it into the power grid. Moreover, inverters monitor essential parameters of the installation, such as voltages, currents, and power. This data is indispensable for purposes such as maximum power point tracking (MPPT), which can be used to optimize the performance of individual solar cells. Moreover, the transducers used in the inverter stations detect power drops caused by line interruptions and other faults at an early stage.
Why Knick ?
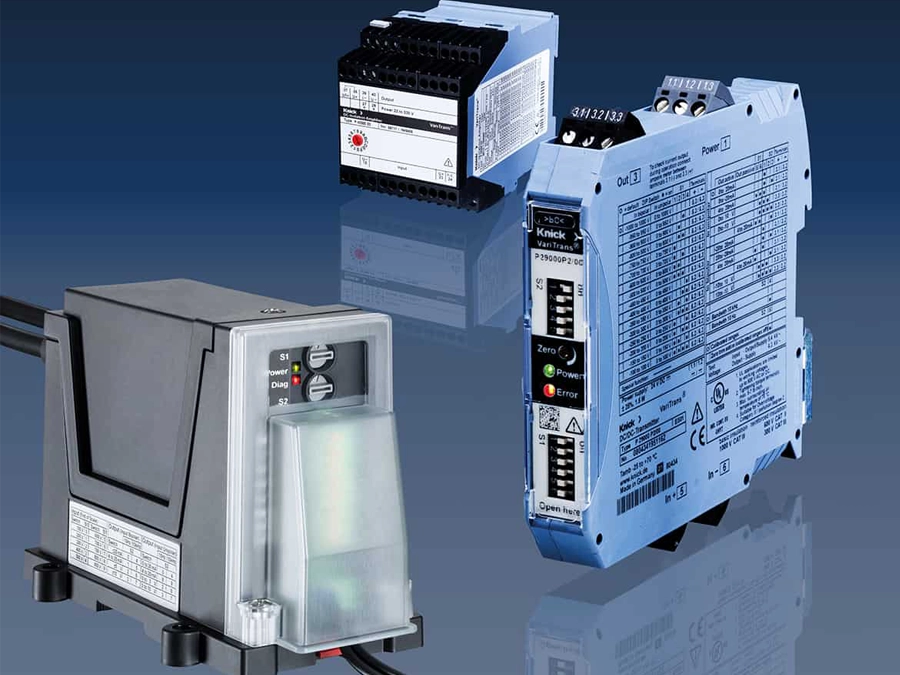
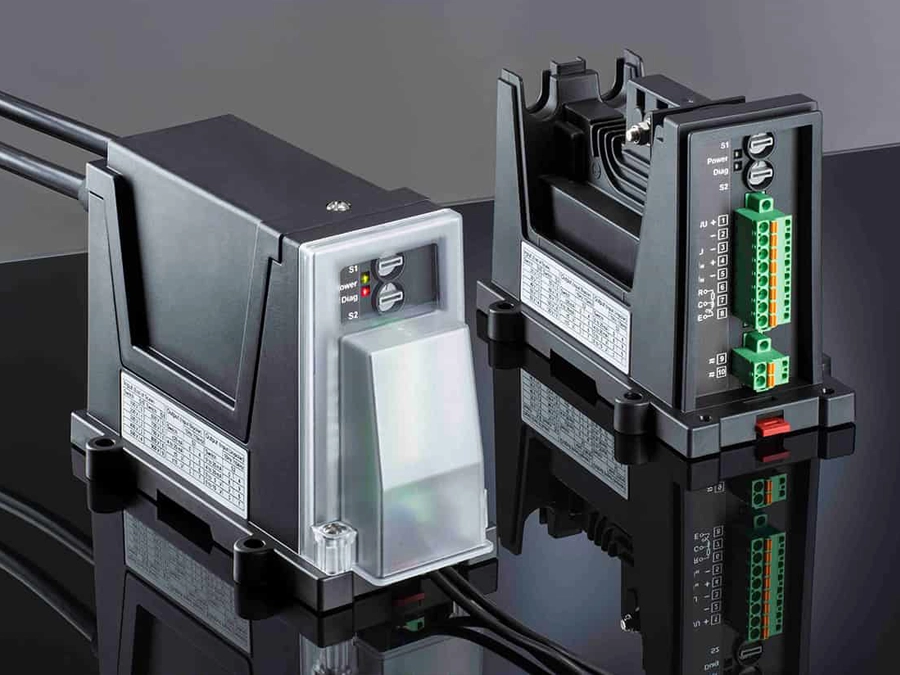
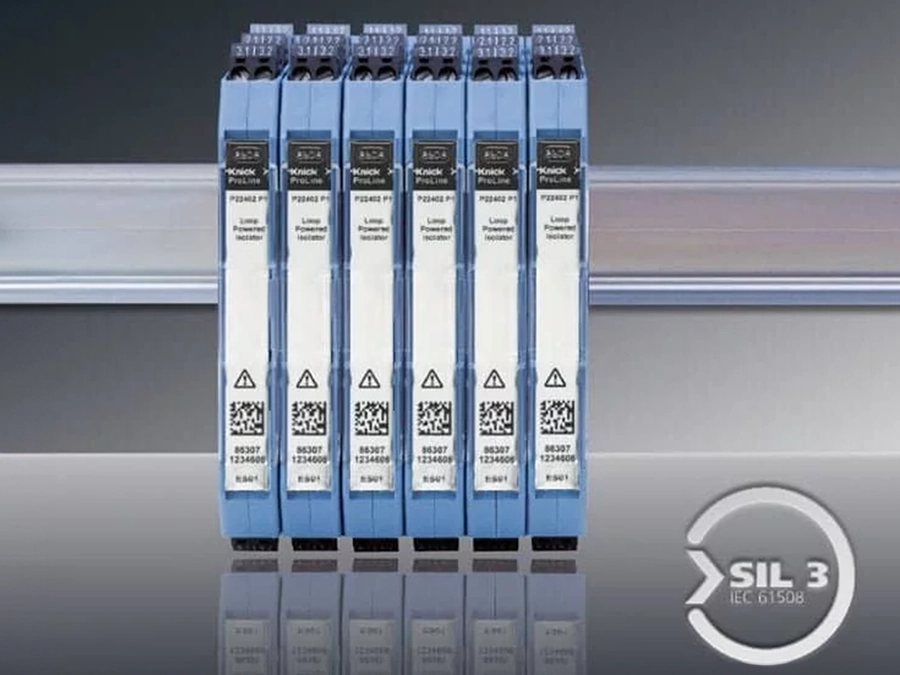
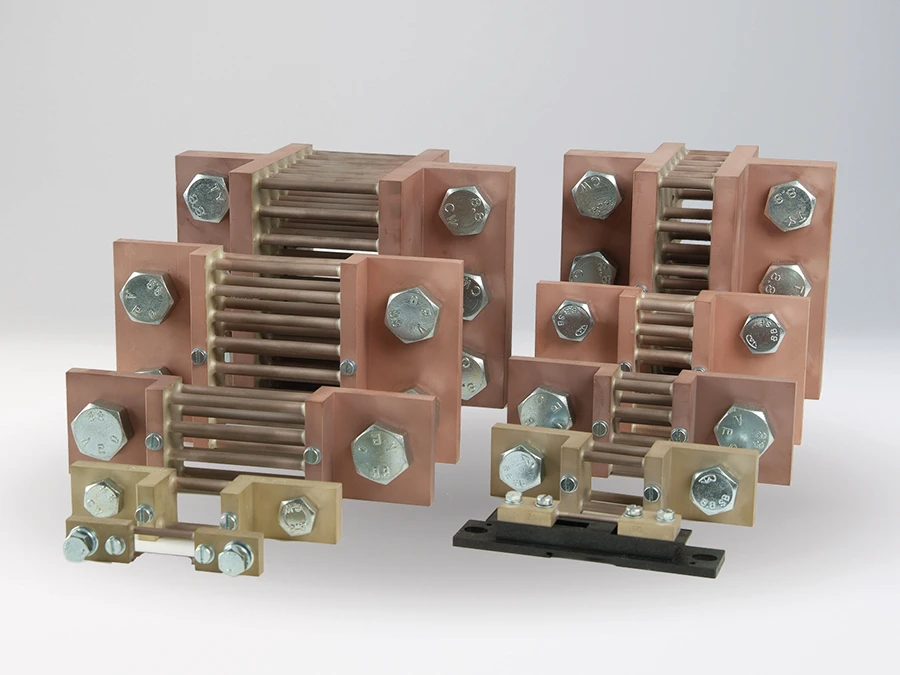
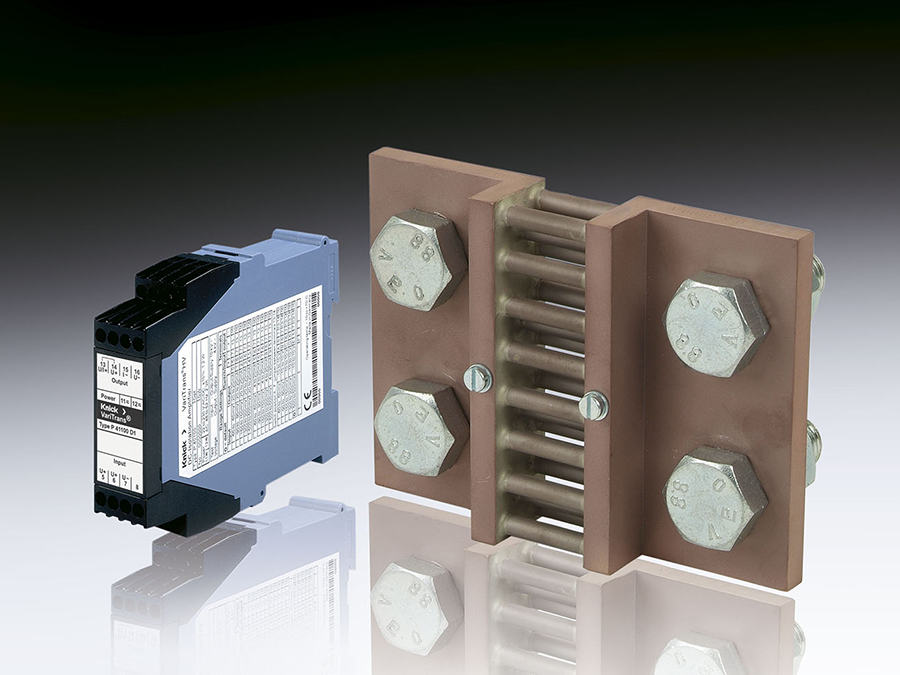
The high voltage transducers of the P40000 family have already demonstrated their reliability in current and voltage monitoring for solar parks. Their reinforced insulation for up to 1,800 V is ideal for PV installations with system voltages of 1,500 V and protects not only downstream control and evaluation systems but also ensures the safety of personnel. Additionally, the product family boasts an exceptionally long mean time between failures (MTBF) of 2,700 years, based on our field data.
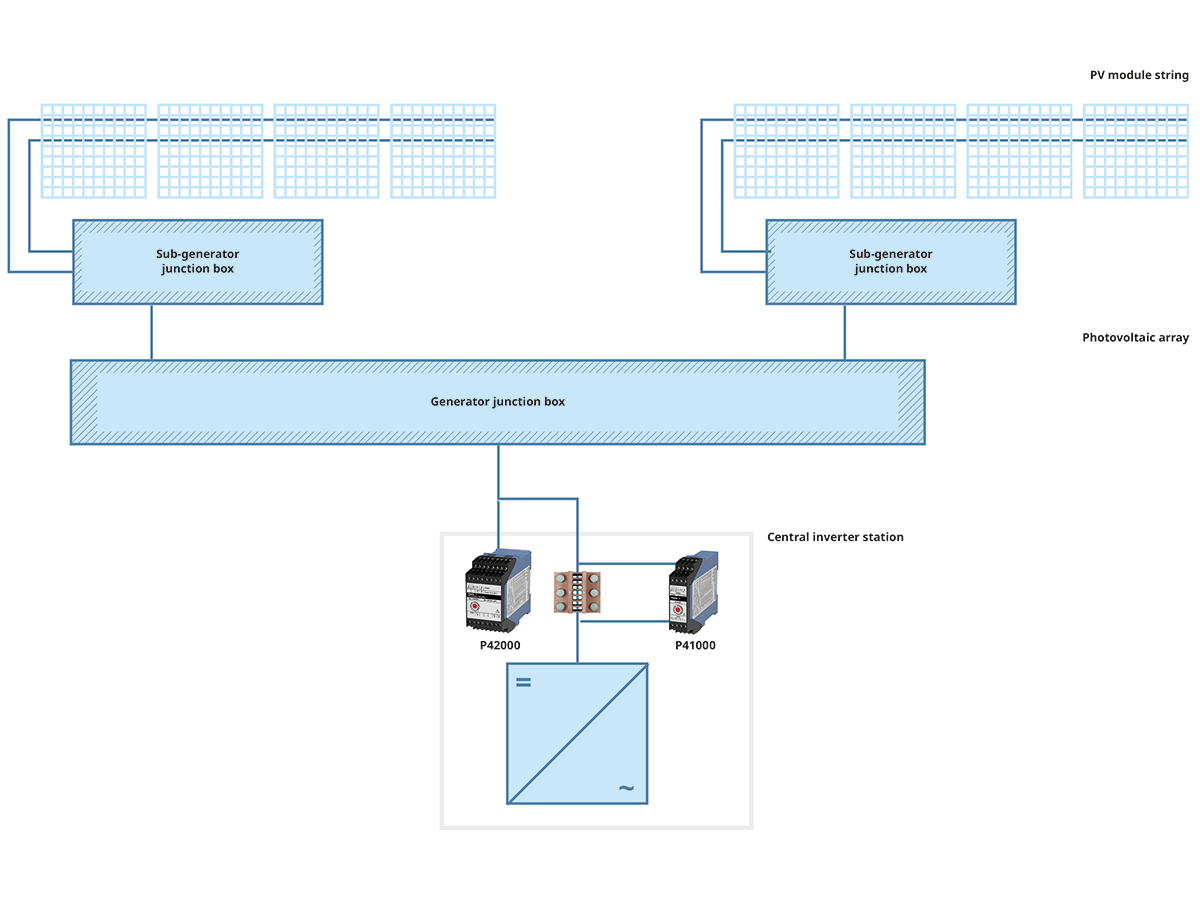
Reduction of Decentralized Measuring Points
If system operators rely on precise high voltage transducers in their inverter stations, monitoring can be centralized in many cases. This saves costs and reduces the number of measuring points that were previously needed on each string, which is a series of PV modules connected in series.
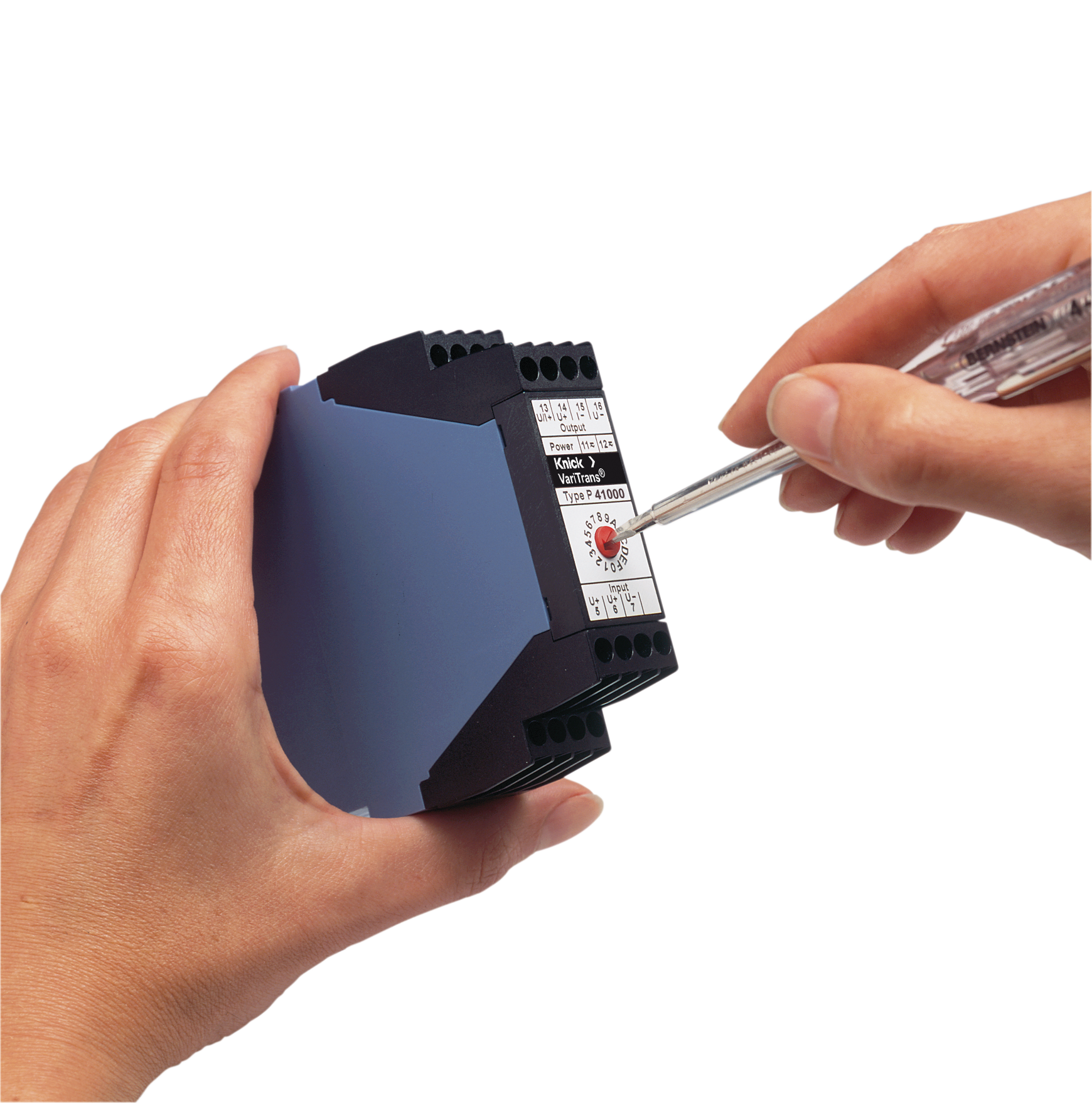
Transducers in the P41000 series monitor currents with a gain error of < 0.1 % and a T90 response time of < 110 μs, transmitting the measured values as a standard signal almost instantaneously to the inverter. This results in an exact total current measurement that enables system operators to detect minor deviations at an early stage and easily localize the reason for the fault in the PV installation.
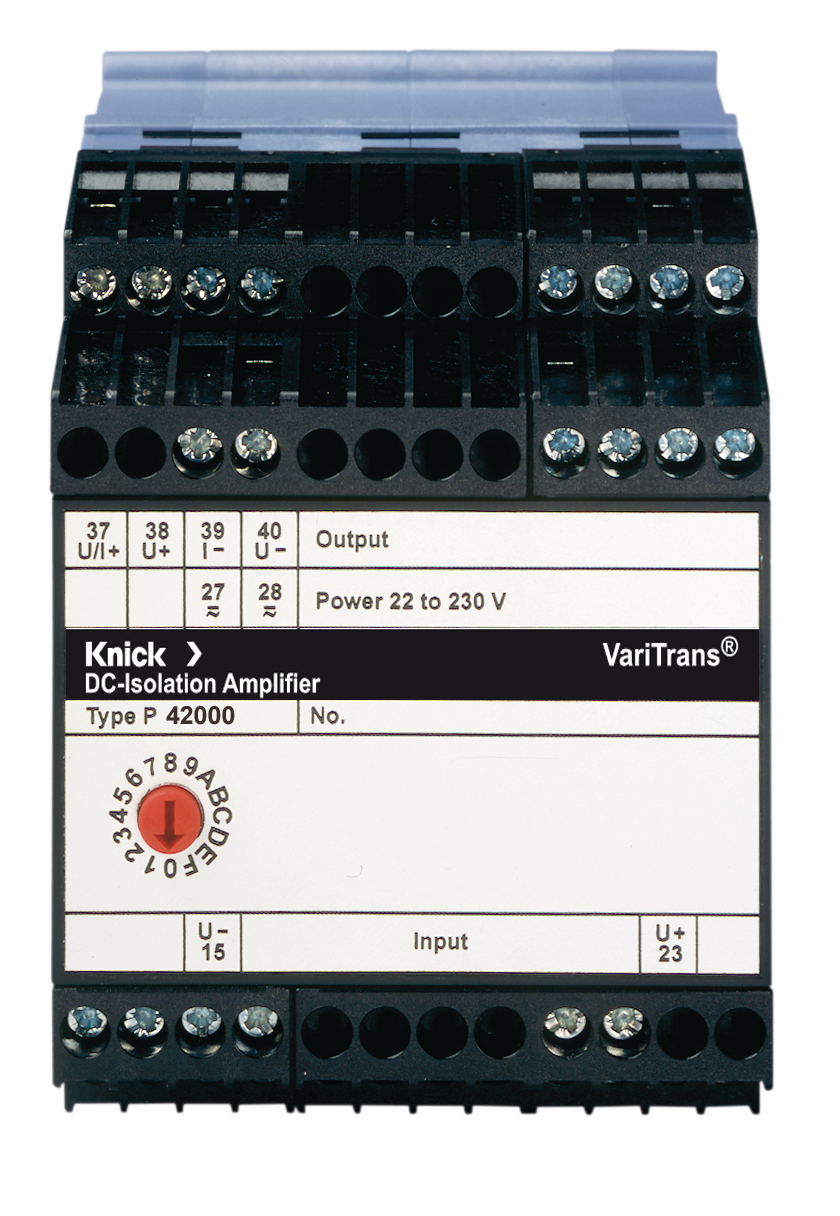
Transducers in the P42000 series have proven themselves in monitoring the (string) voltage. Due to their limited gain error of < 0.3 % and a T90 response time of 110 μs, P42000 devices guarantee precise measured values that facilitate the immediate detection of power losses and potential hazards such as overloads or short circuits.